Intramuscular (IM) Administration
Here are the steps needed to accomplish administering IM injections. Feel free to read through the steps .
- You will be needing all these supplies. Prepare the medication to be given, syringe, alcohol prep pad, gauze, band-aid and needle. The needles are usually 21g or 22g, and 1 1/2″ long.
- Wash your hands.
- Prepare/Mix the medication accordingly and put it into the syringe.
- Attach the new needle into the syringe.
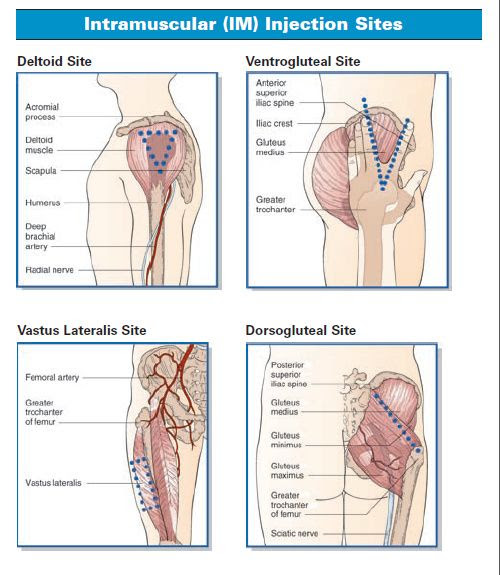
- Medication can be given into the:
- Ventrogluteal – Patient may lie on back or side with hip and knee flexed.
- Vastus lateralis – Patient may lie on the back or may assume a sitting position.
- Deltoid – Patient may sit or lie with arm relaxed.
- Dorsogluteal – Patient may lie prone with toes pointing inward or on side with upper leg flexed and placed in front of lower leg.
- The site should be free of bumps and scars.
- Clean the site with an alcohol pad. Allow the alcohol to dry. Do not use a blower or fan to quicken the drying process.
- Spread the skin with your fingers and inject the needle straight down in a dart-like motion all the way.
- Pull back on the plunger a little. If you see blood enter the syringe, pull the needle out a little and inject the medication. If you do not see blood, simply inject.
- Pull the needle out and dispose of properly in a sharps container. Do not put medical or sharp waste in the regular garbage.
- Use the gauze to dab up any blood, if necessary, and cover with a bandage.
- Wash your hands.
Comments
Post a Comment