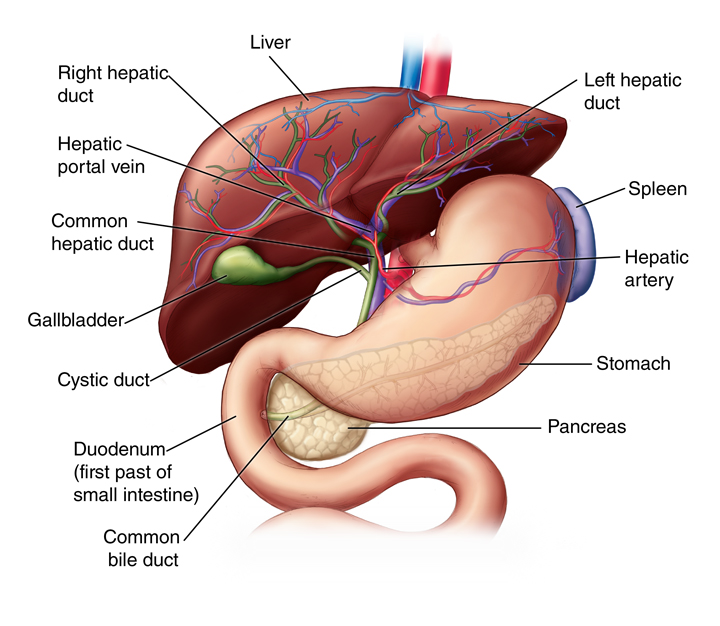
Anatomy of the liver
The liver is located in the upper right-hand portion of the abdominal cavity, beneath the diaphragm, and on top of the stomach, right kidney, and intestines.
Shaped like a cone, the liver is a dark reddish-brown organ that weighs about 3 pounds.
There are 2 distinct sources that supply blood to the liver, including the following:
Oxygenated blood flows in from the hepatic artery
Nutrient-rich blood flows in from the hepatic portal vein
The liver holds about one pint (13%) of the body's blood supply at any given moment. The liver consists of 2 main lobes. Both are made up of 8 segments that consist of 1,000 lobules (small lobes). These lobules are connected to small ducts (tubes) that connect with larger ducts to form the common hepatic duct. The common hepatic duct transports the bile made by the liver cells to the gallbladder and duodenum (the first part of the small intestine) via the common bile duct.
Functions of the liver
The liver regulates most chemical levels in the blood and excretes a product called bile. This helps carry away waste products from the liver. All the blood leaving the stomach and intestines passes through the liver. The liver processes this blood and breaks down, balances, and creates the nutrients and also metabolizes drugs into forms that are easier to use for the rest of the body or that are nontoxic. More than 500 vital functions have been identified with the liver. Some of the more well-known functions include the following:
Production of bile, which helps carry away waste and break down fats in the small intestine during digestion
Production of certain proteins for blood plasma
Production of cholesterol and special proteins to help carry fats through the body
Conversion of excess glucose into glycogen for storage (glycogen can later be converted back to glucose for energy) and to balance and make glucose as needed
Regulation of blood levels of amino acids, which form the building blocks of proteins
Processing of hemoglobin for use of its iron content (the liver stores iron)
Conversion of poisonous ammonia to urea (urea is an end product of protein metabolism and is excreted in the urine)
Clearing the blood of drugs and other poisonous substances
Regulating blood clotting
Resisting infections by making immune factors and removing bacteria from the bloodstream
Clearance of bilirubin, also from red blood cells. If there is an accumulation of bilirubin, the skin and eyes turn yellow.
When the liver has broken down harmful substances, its by-products are excreted into the bile or blood. Bile by-products enter the intestine and leave the body in the form of feces. Blood by-products are filtered out by the kidneys, and leave the body in the form of urine.
Comments
Post a Comment